Frequently Asked Questions
Kidney disease refers to a variety of conditions related to compromised kidney function. This includes acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. Many conditions can be considered the underlying cause loss of kidney function, like high blood pressure, diabetes, lupus disease, IgA nephropathy, and many others.
Acute kidney injury refers to any sudden loss of kidney function.
Some patients do not develop apparent symptoms. Acute kidney injury is noticed on routine labs for other purposes. When symptoms develop, they may include feeling weak, confusion, vomiting, urinating less, blood in the urine, swelling, or shortness of breath.
It is a progressive slow loss of kidney function. CKD typically occurs due to chronic injury of time by chronic disease processes like diabetes and hypertension. If untreated, it may lead to continued loss of kidney function and even dialysis.
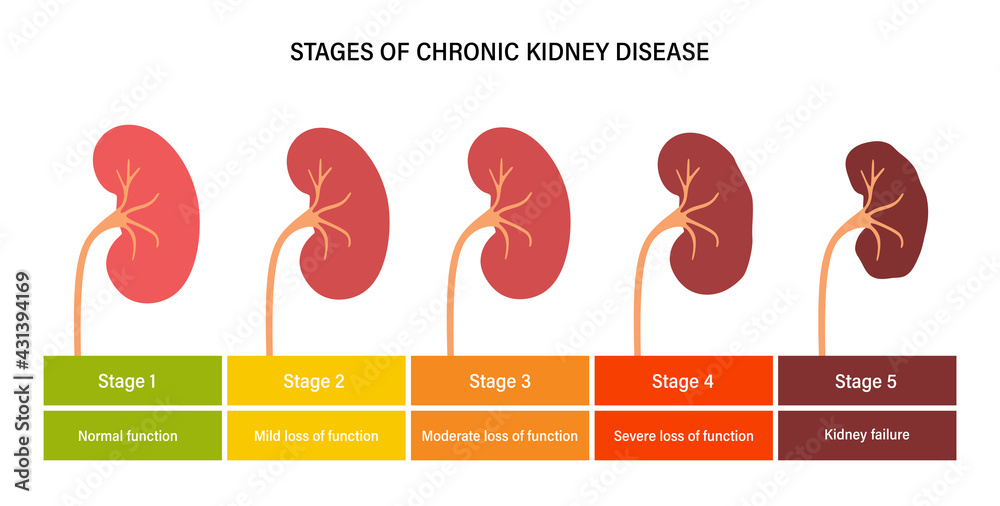
Chronic kidney disease is divided to five stages based on the glomerular filtration rate. Stages 1-3 are considered early stages, while stages 4-5 are advanced stages.
Resources



National Kidney Foundation

AAKP

UpToDate for Patients
